Numbness
Numbness is a loss of sensation in a part of the body. It may be accompanied by symptoms such as a burning or pins-and-needles sensation. Numbness can occur on one or both sides of the body. It may be caused by spinal stenosis -- narrowing of the spinal spaces causing pressure on the nerves.
What causes numbness?
In many cases, numbness is caused by irritation, damage, or compression of the nerves. It often affects nerves on the periphery of the body. Numbness may affect a single nerve or several, as occurs with a herniated disc or carpal tunnel syndrome. Diabetes can also cause numbness, as it can damage nerve fibers (such as those that go to the feet).
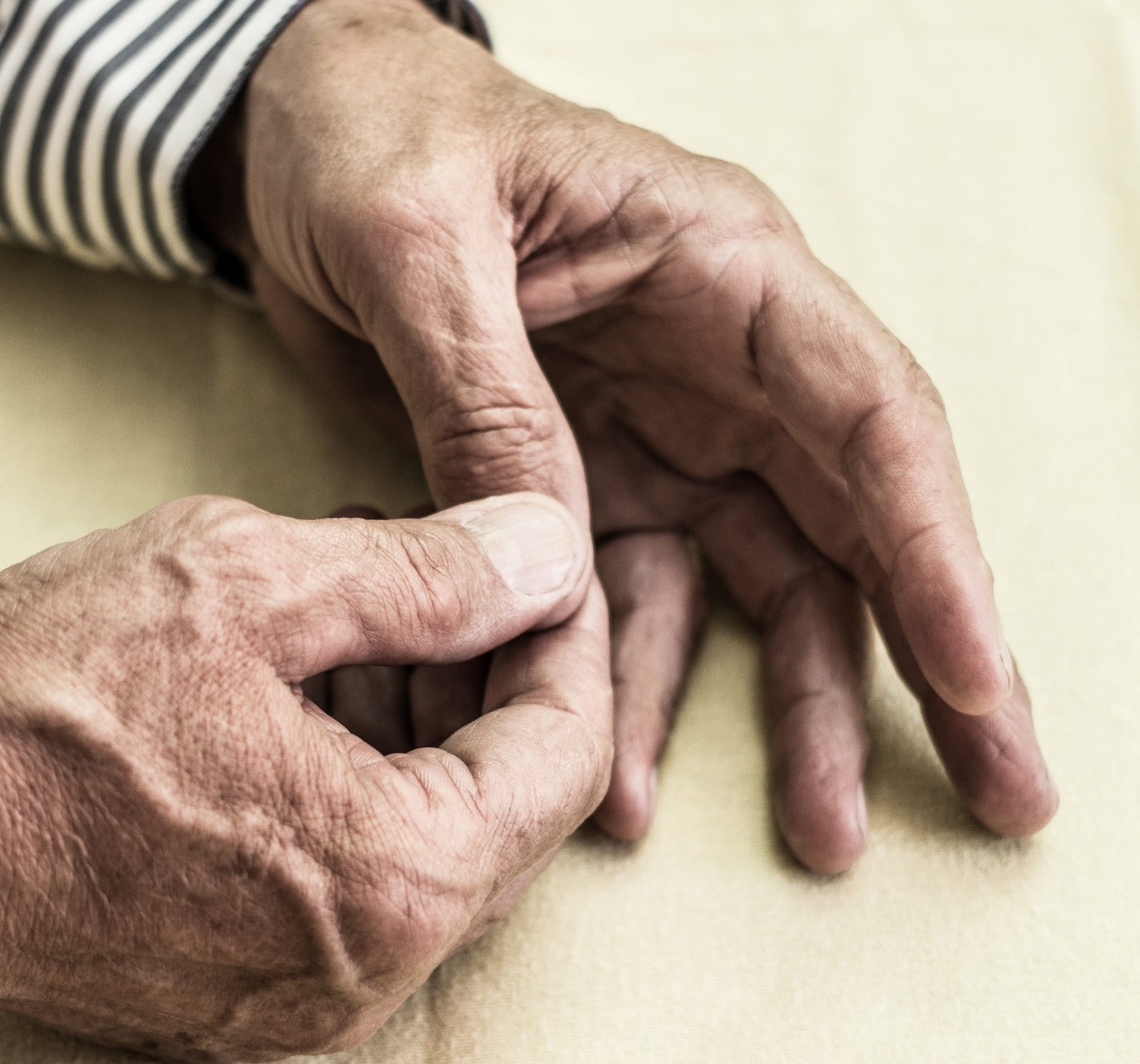

How spinal conditions can cause numbness
Numbness can occur when a part of this pathway malfunctions because of a disorder or a drug. Spinal conditions that cause numbness include herniated disc, degenerative disc disease, and spinal stenosis (narrowing of the passageway for the spinal cord).
For a person to feel sensation, sensory receptors must detect information and send a signal along a pathway:
- Through the nerves (from the skin to the spinal cord)
- Through the spinal nerve roots, formed by thick, short branches of sensory nerves that pass through the vertebrae to connect with the spinal cord
- Up the spinal cord
- Through the brain stem
- To the part of the brain that perceives and intercepts these signals
© Achieve Brain & Spine. All Rights Reserved. Website and Marketing: S3E, Digital Marketing Company Los Angeles