Intracranial Hematoma
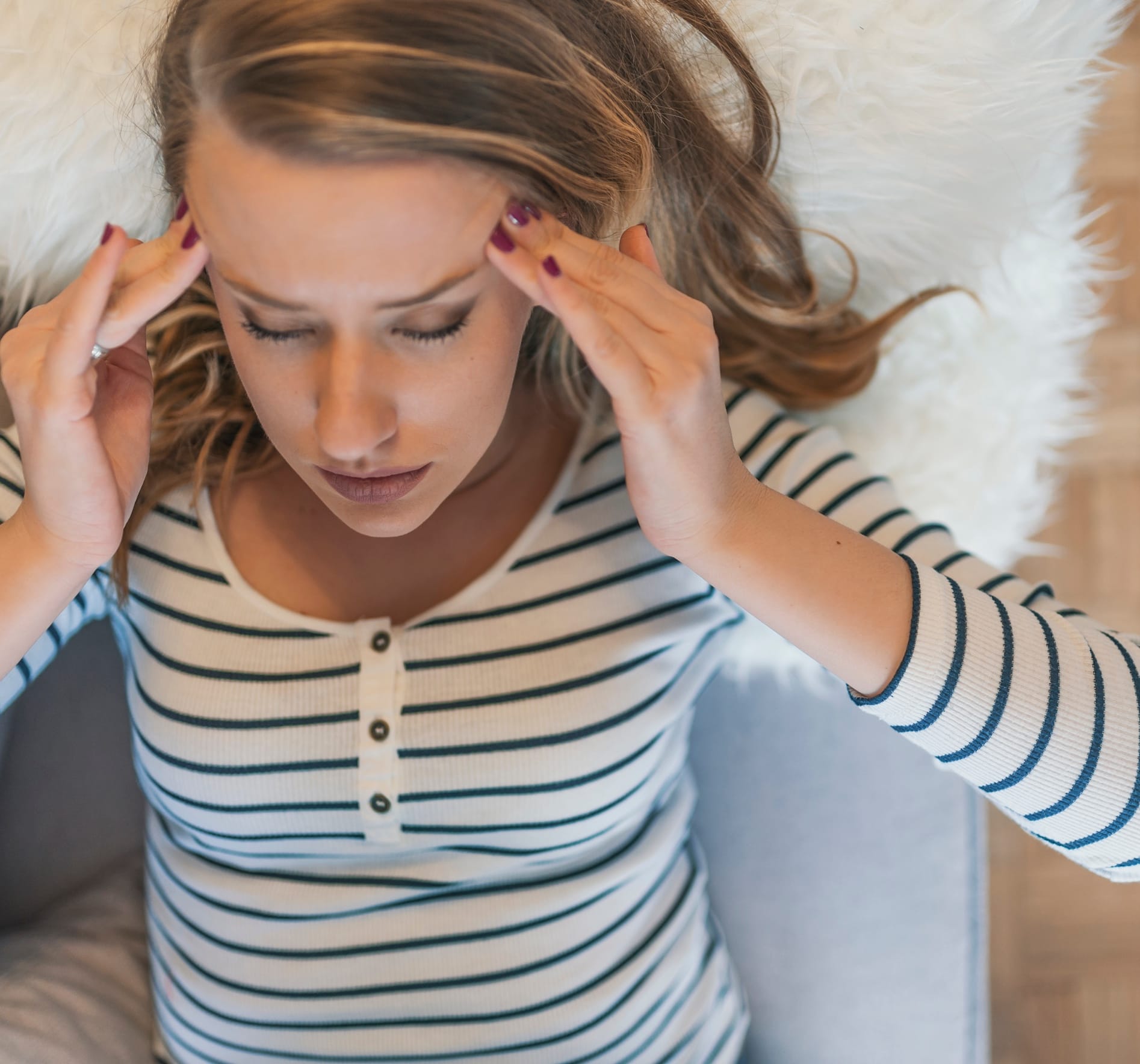
An intracranial hematoma is an accumulation of blood within the skull, often caused by trauma or a ruptured blood vessel in the brain. The blood may be accumulated within the tissue of the brain, or beneath the skull, pressing on the brain. Intracranial hematoma can be life-threatening and requires immediate treatment. The common signs and symptoms can include headache, nausea, vomiting, double vision, lethargy, confusion, somnolence, and inability or impairment of strength on one side of the body.
Common causes of intracranial hematoma
This condition is often caused by injury to the head. Even mild head trauma can cause intracranial hematoma in older adults taking aspirin or an anticoagulant. Common causes of this condition include:
- Falls
- Assault
- Bicycle accidents
- Motor vehicle accidents
- Sports injuries

How is an intracranial hematoma treated?
Although surgery may not be recommended for a small hematoma with no symptoms, you will still need to be carefully monitored, in case symptoms appear days or weeks after the injury.
If you are taking a blood thinner, you may need medications such as vitamin K or fresh frozen plasma or Kcentra to reverse the effects of the medication and reduce the risk of further bleeding in the brain. In many cases, treatment for an intracranial hematoma involves surgery. Surgical treatment options include:
- Surgical drainage: If the hematoma is localized and the blood is not clotting, your surgeon may create an opening through your skull to remove the collected blood called a burr hole.
- Craniotomy: If the hematoma is large, your surgeon may need to open a section of your skull to remove the blood.
© Achieve Brain & Spine. All Rights Reserved. Website and Marketing: S3E, Digital Marketing Company Los Angeles